Ω Probability Calculation Steps
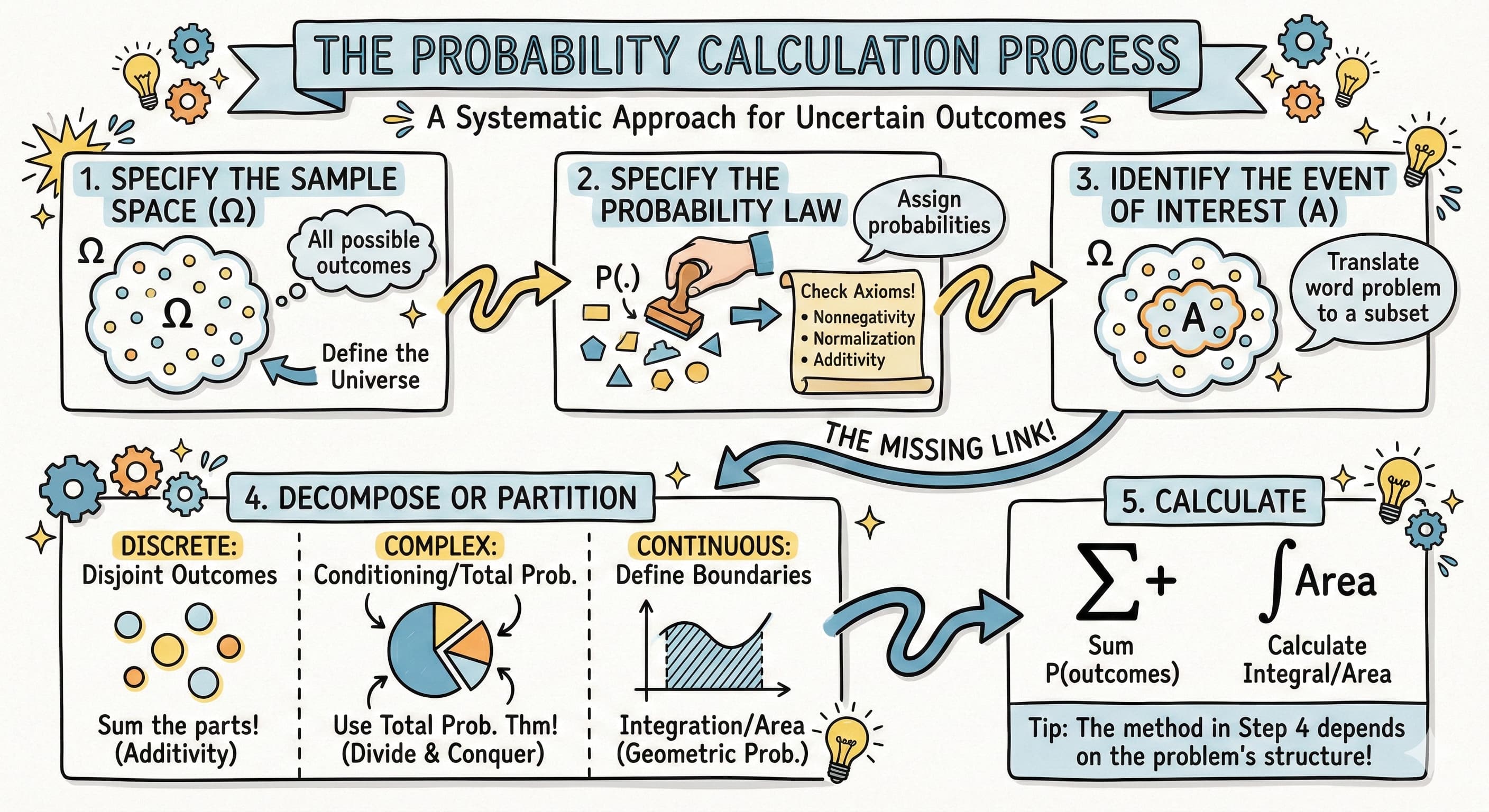
Probability Calculation Steps
- Specify the Sample Space (Ω): Identify all possible outcomes of the experiment.
- Specify the Probability Law: Define the probability for each outcome or region of the sample space, ensuring the axioms are satisfied (nonnegativity, normalization, and additivity).
- Identify the Event of Interest (A): Translate the verbal description of the problem into a mathematical subset of the sample space.
- Decompose or Partition (The "Missing" Step):
- For discrete spaces: Break the event into disjoint outcomes to use Additivity.
- For complex events: Use Conditioning or the Total Probability Theorem to simplify the event into manageable pieces.
- For continuous spaces: Define the boundaries of the event for integration (or geometric area).
- Calculate: Sum the probabilities of the outcomes in the event or calculate the relevant integral/area.
Why the "Decomposition" Step is Crucial
When tackling probability problems, the "Decomposition" step is often the foundation for success. It's the process of breaking down a complex situation into smaller, more manageable parts.
- Counting: If all outcomes are equally likely, this step involves using Permutations or Combinations to find |A| and |Ω|.
- Sequential Models: If the experiment has stages, you use the Multiplication Rule or a tree diagram to find the probability of each path before summing them.
